

Six Sigma Consultation
Six Sigma is a business management strategy originally developed by Motorola, USA in 1981. As of 2010, it enjoys widespread application in many sectors of industry, although its application is not without controversy. Six Sigma seeks to improve the quality of process outputs by identifying and removing the causes of defects (errors) and minimizing variability in manufacturing and business processes. It uses a set of quality management methods, including statistical methods, and creates a special infrastructure of people within the organization.
Six Sigma originated as a set of practices designed to improve manufacturing processes and eliminate defects, but its application was subsequently extended to other types of business processes as well. In Six Sigma, a defect is defined as any process output that does not meet customer specifications, or that could lead to creating an output that does not meet customer specifications.
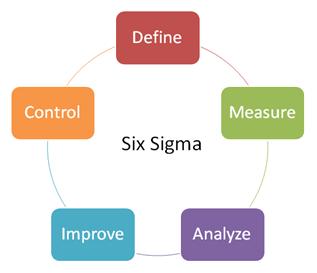
Six Sigma projects follow two project methodologies inspired by Deming's Plan-Do-Check-Act Cycle. These methodologies, composed of five phases each, bear the acronyms DMAIC and DMADV .
• DMAIC is used for projects aimed at improving an existing business process.
• DMADV is used for projects aimed at creating new product or process designs. Within the individual phases of a DMAIC or DMADV project, Six Sigma utilizes many established quality-management tools that are also used outside of Six Sigma.
|
|
GEC provides Lean Six Sigma Consulting services for deployment support to organizations. Our Six Sigma Consulting Services follow the DMAIC or the DMADV methodology as appropriate.GEC has successfully developed Six Sigma deployment strategies and training for Product and Process Development, Manufacturing and Business Process Improvement. Our broad experience across many technologies helped us gain insight on how to apply Six Sigma methods to Business Processes. During deployment GEC provides workshops for managers, business analysts, engineers, process and product developers.
Consulting for Lean Six Sigma Deployment support includes the following:
• Six Sigma Training
• Lean management training and implementation support
• Hand holding and support for initial projects
• support for problem solving
The project selection takes into account amount of effort, risk and possibility of success in a reasonable time frame and impact of results on profits, customer satisfaction and business growth. Most of the projects relate to reducing defects (failure to deliver what the customer wants) or reducing Product or Service Non Compliance or Non conformities (as per specifications or company standards). It is important here to note that the word "customer" relates to internal as well as external customers. A project may relate with improvement of a current process or designing a new process. The two require different roadmaps and approaches. Designing a new process requires a DMADV roadmap which includes Define-Measure-Analyze-Design-Validate steps while improving an existing process requires a DMAIC roadmap (Define-Measure-Analyze-Improve-Control)
Advantages of Six sigma
Based on Data
Ø In Six Sigma, decisions are made based on empirical evidence, not just on assumptions and anecdotal evidence. This includes determining the need for a project, determining the cause of the problem being addressed, and deciding what improvements will be made. In all these cases, data is required for decision making.
Proven Success
Ø Beginning with Motorola, many large companies have successfully rolled out Six Sigma initiatives and driven positive change in their organizations. The results have benefited customers, employees, and shareholders.
Sustainable Solutions
Ø The DMAIC and DMADV processes are specifically designed for sustainable solutions. In DMAIC, the improvements to a process are confirmed with data, and an entire phase is devoted to ensuring that the gains are sustained. In DMADV, which is used for creating new products and processes, a similar mindset holds.
Timeframe
Ø As the saying goes, "Do you want it fast or do you want it right?" In order to effectively use the Six Sigma methodology, a substantial amount of time must be allowed for a project. It does not provide simple fixes, and at times the people involved can become frustrated with the time required to systematically follow the improvement model.
Training Requirements
Ø In traditional Six Sigma implementations, employees go through extensive training to become Six Sigma project leaders (Black Belts and Green Belts) and sponsors (Champions and Process Owners). For the Black Belt role in particular, training can take several weeks or more, and occur over a period of months. This is not feasible in some environments.
Corporate Focus
Ø Although the principles underlying Six Sigma could certainly be made applicable to small business and organizations, it is primarily an option for larger corporate organizations. Overwhelmingly, the majority of training and information available is geared toward that sector. This makes it difficult for other groups to see any benefit in adopting the methodology.
training, consulting, consulting company Kuwait, consulting company Gulf, training GQI, training in kuwait, training Arabian gulf, Environmental consultation, training seminars, iso consultancy, train the trainer, project management training, auditing, Consulting Services, Global Quality Institute for training and development, ISO Training in Kuwait, Management Courses in Kuwait, Consulting Services in the Gulf, Feasibility Study in the Gulf, kuwait, Six Sigma, market plan, feasibility study, statistical for business, ISO consultation, iso consulting, global quality, service quality institute, international quality standards, international quality systems, career training programs, training kuwait, feasibility studies, feasibility study template, project feasibility study, seminars conferences, industrial consultant, industrial consultancy, industrial design consultancy, statistics for business, statistics business, uses of statistics in business, statistic business, environmental engineering consultant, environmental consulting, environmental consultants, environmental consultant









